To help track disk space on a cluster, here's a simple batch script that works on Windows. It accepts a list of hostnames, and outputs the size and free space on each server to a log file.
This is a test server, aptly named "server". 5 drives in Windows Explorer.
The script is available on GitHub; the version at time of writing is here:
@echo off
:: Batch file to log out a local drive report to a .log file in the same directory
:: Log files are named based on the date and time
:: Specify which servers to attempt to return disk space for (delimit with spaces)
:: Enter hostname, and ensure the account running this script has local or domain admin rights
set SERVER_LIST=server
:: Set output date time (YYYYMMDD_hhmmss)
set LOG_TIMESTAMP=%date:~-4,4%%date:~-7,2%%date:~0,2%_%time:~0,2%%time:~3,2%%time:~6,2%
set LOG_DATE=%date:~-4,4%%date:~-7,2%%date:~0,2%
set LOG_TIME=%time:~0,2%%time:~3,2%%time:~6,2%
:: Specify output prefix - this uses an absolute path, if you prefer to use relative then ensure the scheduler includes a "start in" path
set LOG_LOCATION=C:\DriveReport\DriveReport_%LOG_TIMESTAMP%.log
:: Create empty output file
>nul copy nul %LOG_LOCATION%
:: Loop over each server to return stats and append to log file
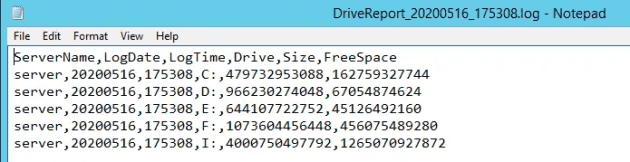
echo ServerName,LogDate,LogTime,Drive,Size,FreeSpace>>%LOG_LOCATION%
for %%i in (%SERVER_LIST%) do (
for /f "tokens=1,2,3" %%a in ('wmic /node:"%%i" LogicalDisk Where DriveType^="3" Get DeviceID^,Size^,FreeSpace^|find ":"') do @echo %%i,%LOG_DATE%,%LOG_TIME%,%%a,%%c,%%b>>%LOG_LOCATION%
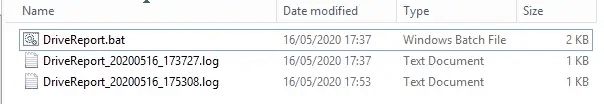
)This outputs one log file per run, containing a row per drive.
One .log file is produced per run of the batch script
Inside, there's a row per drive
This can be scheduled using Windows Task Scheduler and has been tested on Windows 10, Windows Server 2012R2, Windows Server 2016.